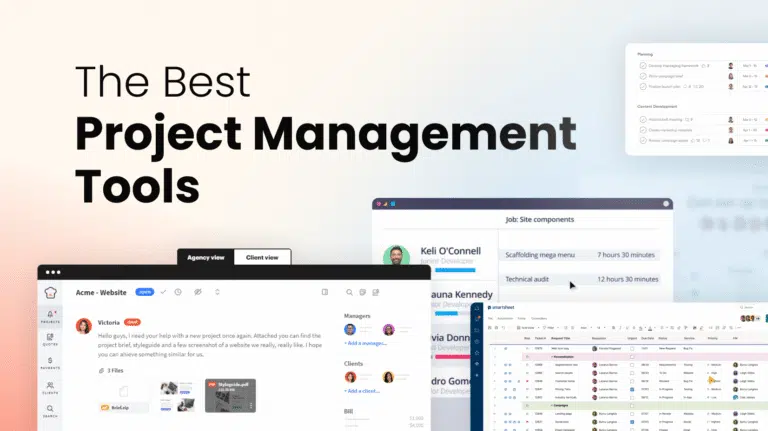
Project management is the art and science of planning, executing, and overseeing a project to achieve specific goals within defined constraints. It’s a critical skill in today’s fast-paced business environment, ensuring that projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards. This comprehensive guide will delve into the essential aspects of project management, including its importance, key methodologies, essential skills, and practical tips for success.
The Importance of Project Management
Effective project management is crucial for several reasons:
- Goal Achievement: It helps in aligning projects with the strategic goals of the organization, ensuring that resources are used efficiently to achieve desired outcomes.
- Resource Optimization: Proper planning and management ensure that resources (time, money, people) are utilized optimally, reducing waste and improving productivity.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks early in the project lifecycle helps in avoiding potential issues that could derail the project.
- Quality Control: Project management frameworks include quality assurance processes that ensure the final deliverables meet the required standards.
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: By managing stakeholder expectations and keeping them informed, project managers can ensure higher satisfaction and support for the project.
Key Project Management Methodologies
Several methodologies guide project management practices. Each has its own set of principles, processes, and tools, tailored to different types of projects and industries. Here are some of the most popular ones:
Waterfall
The Waterfall methodology is a linear, sequential approach where each phase must be completed before the next begins. It’s best suited for projects with clearly defined requirements and scope.
Phases:
- Requirements
- Design
- Implementation
- Verification
- Maintenance
Pros:
- Clear structure and milestones.
- Easy to understand and manage.
Cons:
- Inflexible to changes.
- Not suitable for complex, iterative projects.
Agile
Agile is an iterative approach that focuses on collaboration, customer feedback, and small, rapid releases. It’s ideal for projects where requirements are expected to evolve.
Principles:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools.
- Working software over comprehensive documentation.
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation.
- Responding to change over following a plan.
Pros:
- Flexibility and adaptability.
- Continuous improvement and feedback.
Cons:
- Can be challenging to scale.
- Requires high customer involvement.

Scrum
Scrum is a subset of Agile, designed for teams of ten or fewer members, who break their work into actions that can be completed within time-boxed iterations called sprints (usually two weeks).
Roles:
- Product Owner
- Scrum Master
- Development Team
Events:
- Sprint Planning
- Daily Stand-up
- Sprint Review
- Sprint Retrospective
oosts team morale and motivation.
Conclusion
Project management is an essential discipline that combines art and science to drive successful project outcomes. By understanding and applying the right methodologies, developing key skills, and following practical tips, project managers can navigate the complexities of their projects and deliver exceptional results. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a novice, continuous learning and adaptation are key to mastering the ever-evolving field of project management.